Jan 29, 2009
Strange Hard Disk Issues.
Because I know what I'm doing, I'm perfectly happy with the risks so the RAID will be staying once I get this fixed, but with a nightly backup system in place once I can get hold of a big enough single hard disk.
Anyway, here's the problem: Vista bluescreens just after the point where Windows switches to the Nvidia RAID driver rather than directly accessing the RAID via the BIOS (well, I'm pretty sure that's what happens). In simple terms that's when all the drivers listed when starting safe mode have been loaded, or when (in my case) the hard disk cuts out for about 3 seconds, before resuming booting.
The data on the RAID is still completely intact and without any errors, according to Paragon Partition Manager, which accesses it without the need for a driver. If possible I would like to avoid having to copy the partition to another disk (which I would have to purchase), repair it in some way, and then put it back on the RAID.
The problem began after I ran a Diskeeper Boot-time Defrag - after showing the normal Vista boot screen, the screen went blank with a lot of hard disk activity for about 15 minutes, then Windows started but displayed some very weird behaviour - many services (such as automatic updates and event viewer) refused to start, as did several programs. Assuming it was a temporary error caused by the MFT defragmentation, I restarted the computer and that was when the problem began.
Somehow Diskeeper has managed to make the RAID incompatible with the Nvidia drivers.
Here are some solutions which I have tried:
* Booting from the x86 or x64 Vista setup discs, or the x64 recovery CD (basically a subset of
what is available on the setup disc) - the hard disks make a repetitive noise for about a
minute every time setup attempts to access them and loading the official RAID drivers makes
no difference.
* Booting BartPE - when loading the RAID driver two different floppy drives and 10 floppy
disks have all failed to be read correctly, which suggests a motherboard issue (?)
* Paragon Partition Manager (which is awesome software btw) detected everything and allowed
me to selectively copy some critical files to a flash drive, and if it comes to it, I could copy the
whole partition to a new drive. Running its equivalent of chkdsk /f detected and fixed a few
minor errors (invalid file attributes), but it didn't manage to fix the problem.
Motherboard: Asus P5N-E SLI using the onboard RAID controller.
While purchasing another hard disk to copy the partition to, allowing me to repair it would probably fix the problem and allow me to put it back on the RAID, I would rather avoid having to invest in a new hard disk if possible.
So yeah, if you have any ideas on how to fix whatever is stopping the official Nvidia driver from reading the RAID I would love to hear them
SOLUTION.
For future reference, here is how to fix the problem:
1. Begin installing TinyXP Rev09 (with driverpacks included) on another hard disk or partition.
2. When it gets to the stage where it first reboots during the installation, chkdsk should run on
the faulty partition, fixing the errors and resetting all the file permissions in $Secure.
3. While the partition is now technically in working order as far as the file system is concerned,
the file permissions are all set to the defaults therefore preventing Windows from booting as
certain system files cannot be accessed due to missing permissions. The problem manifests
itself as a black screen with movable mouse cursor (a.k.a. the KSOD). All the normal
solutions to the problem fail, and while secedit with /areas FILESTORE would probably fix
it, it is impossible to run it without actually being in the Windows installation that needs
fixed, which is a pretty big mistake on Microsoft's behalf.
4. To restore the file permissions, create the UBCD4Win with default settings (doesn't really
matter) and boot using it.
5. Next, open MS Explorer, right click the faulty partition, go to the security tab and set
Everyone to have Full Control.
6. Reboot and problem solved.
It took me an entire week, but my computer is now working again (without having to format, or even reinstall Windows)
Articles Source from:-http://hd-data-recovery.blogspot.com/
Jan 26, 2009
What is Data Recovery?
"No one in the data recovery business comes close to challenging Ontrack's leadership. It is by far the most technologically advanced company in the field." - Joe Sullivan, Securities Analyst, Dougherty Summit Securities
Don't assume that your data is unrecoverable; Ontrack provides the following data recovery services recovering lost data:
RDR® - Remote Data Recovery™ Service
Using patented technology, Ontrack engineers perform lab-quality data recovery service right on your server, desktop, or laptop through a modem of Internet connection. Additionally, the connection is secured by using a proprietary communication protocol, encrypted packets, and safe facilities.
In-Lab Data Recovery Service
Ship the damaged drive or storage device to an Ontrack lab and let our experienced engineers determine what is necessary to recover the data. Most standard data recovery jobs are completed in 3-5 days for the fastest turnaround time in the industry, and we return the data on the storage media of your choice.
EasyRecovery™ Professional Software
EasyRecovery Professional provides and easy to use, do-it-yourself solution to meet data loss needs and restore valuable data. EasyRecovery Professional offers a complete solution for disk diagnostic, data recovery, and file repair needs.
Regardless of the Ontrack data recovery option that you chose, you can be sure that:
Ontrack Data Recovery software and data recovery services are complete and safe.
Our engineers pioneered the technology used in this field and continue to produce ground-breaking solutions. You can rest assured that your data is in the most competent hands.
Ontrack data recoveries return current data.
Although many people rely on backups following a data loss, the most recent backup may not be recent enough.
Ontrack Data Recovery software and data recovery services are fast.
Every second that passes following a data loss means time and money. Our data recovery specialists help you quickly determine which data recovery approach is the best for your situation.
Ontrack Data Recovery software and data recovery services are cost-efficient.
The expense in time, money and effort to recreate lost data can be overwhelming to you or your company. We offer a full spectrum of options to meet your budget.
Article source from:-http://www.ontrackdatarecovery.com/what-is-data-recovery/
Mobile Device Data Loss
Data is everywhere. No longer confined to desktop computers, data is always with us – at the gym in the form of an iPod®, in the car via your cell phone, and of course surrounding you at work – notebooks, desktops, servers, etc. With the increased portability of data comes the increased risk for data to be lost, misplaced, damaged or destroyed.
An Ontrack Data Recovery survey conducted among 400 professionals worldwide revealed that 65% of professionals own at least one USB stick. The compact size leads many people to store their sticks incorrectly – in suit pockets or in bags – leaving valuable confidential data at risk.
To help protect mobile devices from data loss, Ontrack Data Recovery has put together some simple preventative steps that will help create good habits for the use of USB sticks and hopefully prevent any data disasters.
1. Minimize misplacement – Try to prevent ‘wandering’ USB sticks. The device is easily lost when you don’t exactly know where it is kept. A dedicated USB spot prevents loss of data from a portable storage device.
2. Carry with care – Make sure your USB is stored safely when traveling to minimize the risk of losing data.
3. No backups, please – A USB stick is too vulnerable to store precious information. These sticks should therefore never be used as a backup device.
4. Put a lid on it – if not in use ensure that the connector of your USB is protected. By using the protective cap, provided with any USB stick, a possible data disaster can be averted
5. Unplug before you leave – Before you embark on a journey that requires a laptop and a USB stick, make sure the devices are separated. This way, both the laptop and the USB stick will run less risk of damage.
Article Source from:-http://www.ontrackdatarecovery.com/mobile-devices-data-loss/
Jan 25, 2009
Boot Sector Viruses Can Damage HDD.
This is a highly simplistic overview of the boot sector function, but it serves our purpose well as it underscores the critical nature of the MBR and boot sector.
Obviously, a boot sector or MBR virus that invades this space on the disk puts the entire operation of that disk at risk.
A boot sector virus is spread via infected floppy disks. This typically occurs when users inadvertently leave a floppy disk in drive A. When the system is next started, the PC will attempt to boot from the floppy. If the disk is infected with a boot sector virus, that virus will infect the boot sector of the user's local drive (C). Unless the floppy disk happens to be a bootable system disk, the user will simply see a standard warning that the drive contains a "non-system disk or disk error" and the user will be prompted to "replace the disk and press any key when ready".
This is a standard error message and is not in and of itself indicative of a boot sector infection. All it means is that a non-bootable disk is contained in the drive the computer is first trying to boot from.
Most users will realize a floppy has been left in the drive, remove it, and reboot the system, unaware they may have just infected their system with a boot sector virus. Of course, if the disk was bootable, they would not receive the error noted above, but will simply be booted to a DOS screen.
Care should be taken to ensure that any bootable floppies have been checked for the presence of boot sector viruses and these disks should be write-protected to ensure no future infection takes place.
Even non-bootable disks can spread a boot sector infection when they are accessed. Further, a boot sector infected hard drive will also infect any floppies used in the system. Where applicable, use write-protected floppies to protect against this.
To write-protect a floppy disk, hold it so that the metal plate is facing downwards. Along the top edge there may be an “open” square. Look closely and you will find a small cover that can be pushed back and forth over the open square. If the cover is closed, i.e. the square is covered, the disk can be written to. If the cover is open, i.e. the square is not covered, the disk cannot be written to and is considered write-protected.
Of course, you would not want to write-protect floppies you use to copy files to, as you would receive a write protection error the next time you attempted the copy.
Most of today’s PCs no longer seek out the floppy drive during bootup, instead using the CD-ROM drive as the first boot device. This can be configured via the system CMOS screen to change the boot sequence to check the hard drive first, the CD-ROM drive second, and the floppy drive third, if at all.
Changing settings in CMOS incorrectly can result in system failure and should not be attempted by inexperienced users. Instructions for accessing the CMOS configuration screen for your PC can generally be found in the motherboard manual.
The first boot sector virus was discovered in 1986. Dubbed Brain, the virus originated in Pakistan and operated in full-stealth mode, infecting 360Kb floppies.
Perhaps the most infamous of this class of viruses was the Michelangelo virus discovered in March 1991. Michelangelo was a MBR and boot sector infector with a March 6th payload overwriting critical drive sectors. Michelangelo was the first virus to attract a large amount of media focus.
Article source from:-http://hdddatarecovery.blogspot.com/2008/12/boot-sector-viruses-can-damage-hdd.html
Jan 24, 2009
Emergency Data Recovery.

Jan 22, 2009
Hard Drive Recovery Information.
Any interface: (IDE, EIDE), Serial ATA (SATA), SCSI, SAS, and Fibre Channel
Any combination of drives: single hard drive or multiple RAID drives
Any brand
Thousands of IT professionals and technology users trust Ontrack Data Recovery services with seemingly unrecoverable data.
Lost data can be recovered in no time whether the hard drive has crashed, has been damaged or has been the victim of a natural disaster. Chat live now
Why Do Hard Drives Lose Data?
if(typeof(lpMTagConfig.dynButton)!="undefined")
lpMTagConfig.dynButton[lpMTagConfig.dynButton.length] = {"name": “chat-sales-english-text”,"pid":"chat-sales-div", 'ovr':'lpMTagConfig.db1'};
Ontrack Data Recovery engineers classify hard drive data loss in two categories:
Logical failure - the hard drive is in working order but some files or data cannot be accessed for logical reasons such as a lost partition or accidental reformatting.
Mechanical failure - the hard drive is not functioning. The most common causes are head crashes and motor failures.
What Causes Hard Drive Failure?The list of incidents causing hard drives to fail and lose data is not limited, but some of the main causes that Ontrack Data Recovery services recover from everyday include power surges, overwriting, physical damages, natural disasters, and viruses.
How Ontrack Data Recovery Services Helps to Recover From Hard Drive Data Loss
Data recovery involves more than just replacing parts. Ontrack Data Recovery services use cutting-edge hard drive recovery tools and processes that come from heavy investment in R&D and 20 years experience. A sample of the expert techniques used include:
In case of mechanical failure, hard disk recoveries are performed in dust-free cleanroom environments where they are carefully dismounted, examined and processed.
Hard drives are imaged. A copy of the disk is made and transferred to a new system.
Ontrack Data Recovery tools can “force” the drive to read around the bad area.
NOTICE: Trying this on your own or through an inexperienced provider may lead to further damage to the drive.
Article Source. www.ontrackdatarecovery.com
Database Recovery Information.
Ontrack Data Recovery service offers a pre-service data recovery evaluation that enables you to know exactly what data you’ll get back before making decisions to proceed with a recovery service. Chat live now
Database Recovery Capabilities
Ontrack Data Recovery services offer multiple data recovery service options for database recovery and are available for:
SQL Server
Exchange Server database
SharePoint Database
Visual FoxPro DBF Database
Interbase Database
Paradox Database
Sybase Database
Oracle Database
MySQL Database
FileMaker Database
Lotus Notes Database
BizTalk Database
And more...
Database Recovery - Causes of Data Loss
Hardware damage at the storage device level (hard disk, SAN or RAID)
File system level damage - controlled by the operating system, the file system stores and organizes system and user files.
File level damage - data loss can occur within the file itself if the internal structure is corrupt.
Database / Information Store Recovery Process
Inaccessible Files
Extract data if storage device is not operational
Adjust or repair file system structures to allow access to the database files
Recover RAW database fragments and rebuild database files
Corrupt Data, Missing Data or Deleted Data
Analyze complex internal structure of the databasewith Ontrack Data Recovery database toolset
Report which items are recoverable (tables and rows,mailboxes, etc.), including deleted data
Extract data from the corrupted database / information store and copy out
Ontrack Data Recovery remote data recovery services are the fastest solution for database recoveries. The remote process will copy the recovered data into a database server that is setup on the client's site.
Article Source. www.ontrackdatarecovery.com
Jan 20, 2009
Data Protecting Technologies.
1.SMART Technology
SMART, also called Self-Monitoring Analysis and Report Technology, mainly protects HD from losing data when there is some problems on the HD. SMART drive can reduce the risk of data loss, it alarms to predict and remind thus enhancing the data security.
2.SPS
Shake Protecting System, can prevent the head from shaking thus enhancing the anti-knock characteristics of HD, avoiding damages caused by shake.
3.DFT
DFT, a kind of IBM data protecting technology, can check hard disk via using DFT program to access the DFT micro codes in hard disk. By DFT, users can conveniently check the HD operation.
4.Floppy disk array technology
Originally ‘Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks’. A project at the computer science department of the University of California at Berkeley, under the direction of Professor Katz, in conjunction with Professor John Ousterhout and Professor David Patterson.
The project is reaching its culmination with the implementation of a prototype disk array file server with a capacity of 40 GBytes and a sustained bandwidth of 80 MBytes/second. The server is being interfaced to a 1 Gb/s local area network. A new initiative, which is part of the Sequoia 2000 Project, seeks to construct a geographically distributed storage system spanning disk arrays and automated libraries of optical disks and tapes. The project will extend the interleaved storage techniques so successfully applied to disks to tertiary storage devices. A key element of the research will be to develop techniques for managing latency in the I/O and network paths.
The original (‘Inexpensive’) term referred to the 3.5 and 5.25 inch disks used for the first RAID system but no longer applies.
The following standard RAID specifications exist:
RAID 0 Non-redundant striped array
RAID 1 Mirrored arrays
RAID 2 Parallel array with ECC
RAID 3 Parallel array with parity
RAID 4 Striped array with parity
RAID 5 Striped array with rotating parity
The basic idea of RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is to combine multiple inexpensive disk drives into an array of disk drives to obtain performance, capacity and reliability that exceeds that of a single large drive. The array of drives appears to the host computer as a single logical drive. The Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) of the array is equal to the MTBF of an individual drive, divided by the number of drives in the array. Because of this, the MTBF of a non-redundant array (RAID 0) is too low for mission-critical systems. However, disk arrays can be made fault-tolerant by redundantly storing information in various ways.
5.SAN
SAN, called Storage Area Network or Network behind servers, is specialized, high speed network attaching servers and storage devices. A SAN allows "any to any" connection across the network, using interconnect elements such as routers, gateways, hubs and swithes. It eliminates the traditional dedicated connection between a server and storage, and concept that the server effectively "owns and manages" the storage devices. It also eliminates any restriction to amount of data that a server can access, currently limited by the number of storage devices, which can be attached to the individual server. Instead, a SAN introduces the flexibility of networking to enable one server or many heterogeneous servers to share a common storage "utility", which may comprise many storage devices, including disk, tape, and optical storage. And, the storage utility may be located far from the servers which use it.
6.NAS
NAS is Network Attached Storage. It can store the quick-increased information
.Backup means to prepare a spare copy of a file, file system, or other resource for use in the event of failure or loss of the original. This essential precaution is neglected by most new computer users until the first time they experience a disk crash or accidentally delete the only copy of the file they have been working on for the last six months. Ideally the backup copies should be kept at a different site or in a fire safe since, though your hardware may be insured against fire, the data on it is almost certainly neither insured nor easily replaced.
7.Backup
Backup in time may reduce the danger and disaster to the lowest, thus data security can be most ensured. In different situations, there are different ways. Both backing up important data of system with hardware and backing up key information with cloning mirror data to different storage device can work well.
Copyright © 2006 CHENGDU YIWO Tech Development Co.' Ltd. All Right Reserved 10Data Recovery E-Book V1.5 (Visit http://www.easeus.com for more information)
Jan 19, 2009
DATA LOSS.
Actually, there are various reasons that cause data loss; software hardware, factitious, natural, intended, unintended, all may cause data loss or damage on storage devices.
Generally, There are two main reasons for data problem: software and hardware whose corresponding reasons are software reason and hardware reason.
1. Software Reason.
Virus, format, mis-partition, mis-clone, mis-operation, network deletion, power-cut during operation all may be the software reasons. The symptoms are usually mis-operation, read error, can not find or open file, report no partition, not formatted, password lost and troubled characters.
A: Computer Viruses: some malicious virus programs will destroy data, overwrite, or erase the data contents.
B: Mis-format: fast or completely format partition, thus changing the file system form ( NTFS, FAT32) of partition.
C: Mis-Clone: when backing up the hard disk, mis-clone or overlay the original data on hard disk.
For these, we can use software tools to recover it . So called soft recovery means data can be recovered by software, not referring to hardware fixing operation for its fault is not because of hardware failure.
The following are prompts that system can not start up normally:
Invalid Partition Table: invalid partition table information.
Missing Operating System: "55AA" mark in DOS boot sector lost or DBR corrupted.
Disk Boot Failure: System file read failure.
Bad or missing command interpreter: Can not find command.com file or ' COMMAND.COM' file corrupted.
Invalid system disk: DOS boot record corrupted.
Type the name of the command, Interpreter: DOS partition mark in partition table error or 'COMMAND.COM' file lost, corrupted.
Error Loading Operating System: Main boot startup program read boot sector unsuccessfully.
Not found any active partition in HDD: Active partition mark in partition table changed as inactive partition mark.
2. Hardware Reason.
Sometimes data loss is because of hardware, such as bad sector in hard disk, power cut, head damage, circuit panel problem, etc.
When your hardware has some problems, you probably will find: the speed of hardware become slow. you cannot operate successfully; you cannot read data, etc, which are most often physical bad track failures.
Correspondingly, data recovery in hardware fix is considered as hard recovery, such as memory medium damage, track damage, hard disk scrape, head damage, electric machinery damage, chip burnout and so on..
The most distinct feature or difference between soft recovery and hard recovery is whether the memory medium itself can be normally accessed by fixing or replacing parts.
Data Recovery E-Book V 1.5 ( visit http://www.easeus.com for more information)
Copyright 2006 CHENGDU YIWO Tech Development Co. Ltd. All Right Reserved.
Jan 18, 2009
Elementary Knowledge of Data Recovery.
Connotation of data is compprehensive, it includes not only multi-media files such as data documents, images, voices that stored in file system or data base, but also hardware inforamtion, network addresses and network services, which are used to deposit and manage those information.
2. The essence of data recovery.
Data recovery means retrieving lost, deleted, unusable or inaccessible data that lost for various reasons.
Data recovery not only restores lost files but also recovers corrupted data.
on the basis of different lost reason, we can adopt different data recovery methods. There are software and hardware reasons that cause data loss, while we can recover data by software and hardware ways.
Being different from prevention and backup, data recovery is the remedial measure. The best way to insure the security of your data is prevention and backup regularly. To operate and use your data accourding to the normative steps, you can reduce the danger of data loss to the lowest.
3. The scope of data recovery.
There are so may forms and phenomenon on data problem, we can divide the objects or scope of data recovery according to different symptoms.
System Problem
The main symptom is that you cannot enter the system or the system is abnormal or computer closes down. There are complex reasons for this, thus we need adopt different processing methods. Reasons for this symptom may be the key file of system is lost or corrupted, there is some bad track on hard disk, the hard disk is damaged, MBR or DBR is lost, or the CMOS seting is incorrect and so on.
Bad track of hard disk
There are logic and physical bad track. Logic bad track is mainly caused by inforrect operation, and it can be restored by software. While physical bad track is caused by physical damage, which is real damage, we can restore it by changing the partition or sector. When there is physical bad track, you'd better backup your data for fear that the data can not be used any more because of hte bad track.
Partition problem
If partition can not be identified and accessed, or partition is identified as unformatted, partition recovery tools such as Partition Table Doctor can used to recover data.
Files loss
If files are lost because of deletion, format or Ghost clone error, files restoring tools such as Data Recovery Wizard can be used to recover data.
Password loss
If files, system password, database or account is lost, some special decryption tools that correspond to certain data form such as Word, Winzip can be sued.
Files repair
For some reasons, some files can not be accessed or used, or the contents are full of troubled characters, the contents are changed so as they can not be read. in this condition, some special files restoring tools can be tried to restore the files.
4. The Principle of data recovery.
Data recovery is a process of finding and recovering data, in which there may be some risk, for no all situations can be anticipated or prearranged. It means maybe there will be some unexpected things happen. So you need reduce the danger in data reovery to the lowest:
Backup all the data in your hard disk
Prevent the equipmet from being damaged again
Don't write anything to the device on which you want to recover data
Try to get detailed information on how the data lost and the losing process Backup the data recovered in time.
Data Recovery E-Book V 1.5 ( Visit http://www.easeus.com for more information)
Copy right 2006 CHENGDU YIWO Tech Development Co. Ltd. All Right Reserved.
Jan 17, 2009
Hard Disk Bad Sectors.
While logical bad sectors can easily fixed using particular software, physical bad sectors can be irreparable. But it doesn't mean there is absolutely no hope, there is still a chance to recover the bad sectors depending on how "deep" the bad sectors are. So, below I am going to consider only physical bad sectors, their symptoms, reasons for appearing, types and ways for possible maintenance.
There are mainly two symptoms you can come across with:
1. Blue screen of death appears often showing the error code indicating that a memory read attempt failed. It follows with inevitable restarting and the next blue screen follows pretty soon with similar error code again. The same message is displayed when there is a problem with DDR memory. But memory modules are easily replaced, or even repaired by replacing the bad chip.
2. Operating system doesn't boot with a message showing that some system files can't be found.
One of the reasons for bad sectors is that some areas of HDD, which are most often used, "wear out" and become harder to read and finally, completely inaccessible. Though it is possible to "recover" these sectors using some applications, it is better to get a new HDD for usage as the main system drive and the repaired one use for other purposes. The reason is that even though the bad sector is fixed, all your data is safe and the HDD is working again, there is a risk that the previous or the next sectors are also about to crash soon. Using for additional storage purposes is not the worst choice for such hard drive.
Another reason for physical bad sectors is a shock, which exceeds the acceptable limits, especially, inflicted while the HDD is operating. In this case numerous bad sectors are almost unavoidable. Usually, after such an accident HDD comes to an absolutely useless condition, when it will keep making a specific sound trying to start spinning, but never will. Imagine a disk rotating with the velocity of over 5000 rpm. Is it possible to make a single dot on it by touching it with, let's say a pencil? The answer is "No". It is absolutely impossible to avoid a nice clear circle instead of a dot. For an HDD such a circle means a huge area of storage, which is inaccessible.
Nowadays, the HDDs have average size of 500 GB and the price ranges around $70. This is an affordable price, but the information contained in HDD might be more expensive. So, such problems as described above need some solutions, and favorably with positive results. As I mentioned, depending on the situation you are, you can use software, which in most cases are helpful. These kinds of applications are able to access the drive regardless the file system and recover the data and even the bad sectors. If you are not sure or it seems that the HDD is completely dead, probably, it is better to have the job done by a professional.
Article Source:-http://hd-data-recovery.blogspot.com
A unique Data Recovery Problem Talking with Data Recovery Specilits.
I have a Problem with my hardisk, I lft my PC unattended for about a hour, when I returned I saw this Blue screen which said something about Some error has occurred and that windows has Halted the system.
rebooted, and when I rebooted I saw the Dos Screen stuff saying detecting IDE Master Slave etc etc. After several minutes it said to insert Boot up disk, but I tried the Windows Disk and after it reached Repair Windows I selected that, but it just remained like that. Tried rebooting a few time and the Same Scenario occurred.
Thank Goodness I had a Spare hard Drive (with Win XP that I made on this same PC) I Hooked this up and removed the (Main original C: drive that was not Booting)
also Hooked the Original Drive in a HD Enclosure and plugged into the USB port as an External Drive. (The Lite went on the Hardrive spins) When I checked "My Computer" it showed the Drive (Now as E) but when I looked at the Properties it said that the Drive was O bytes and the File System was "RAW".
I just cant understand how my NTFS files changed to RAW? in an hour?I even went into Disk Management and it did not show the drive (Only the new C drive)
Downloaded Easeus Data Recovery, it also recognized the Drive as Raw but cud not recover do anything more. Even tried Stellar Phoenix Windows Data Recovery and PTDD Partition Table Doctor 3.5 and they dont even see the Drive.
My question is , Can someone one Recommend how I can recover my important file I saved on it, (A few Hundred MB) Since I dont want to discard the drive.
PC Has Win XP SP2, 2Gb RAM, Hardive Seagate 250GB, any other info needed please let me know.
Please Help me I have important files to recover.
So. See the conversation which we passed.
Me: the drive sounds like it is dead. You can recover the data by rebuilding the disks into another drive, but there is no normal method.
Aslam:Have you tryed to hook that HDD to other PC? Your firend's maybe?
Kamran:No Luck yet, Tried freezing for 12 Hrs, Went it thrawed out Hooked it up again, Still recognized the whole Drive content as RAW file. Cant understand how aDrive cud just change all files to unreadable RAW files.
Mansoor:its very hard to do something effective now. what i would do from now on is that u do ur self a big favor and buy ur self one or two external hard drives. make an image of ur HD every 3 weeks or so than that way u would never lose data.
Muneeb: don't let it thaw
hook it up immediately upon removal from the freezer.
if it warms up and stops reading you may need to re-freeze
Asad:I dunno if this will help, but i reformatted my hard disk a while ago and it also had that problem of raw data. There'd be like 300 gigs usable, and the other 400 gigs as a RAW. I used active parition recovery and it somehow recognized it as a logical partition. Maybe that'll help. Best of luck.
Article Source. http://hd-data-recovery.blogspot.com
Jan 16, 2009
Flashnul - USB / Flash Drive Diagnostic Tool.

___________________6.55____#4436314248563752202020202020202020202020#{53f56307-b6bf--11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b}

Download Flashnul (Windows NT, 2000, XP, Vista)
Hard Disk Failure Messages.
IDE Hard Drive Failure Messages:
• 1701 Fixed disk general POST error
• 1702 Drive/controller time-out error
• 1703 Drive seek error
• 1704 Controller failed
• 1705 Drive sector not found error
• 1706 Write fault error
• 1707 Drive track O error
• 1708 Head select error
• 1709 Error Correction Code (ECC) error
• 1710 Sector buffer overrun
• 1711 Bad address mark
• 1712 Internal controller diagnostics failure
• 1713 Data compare error
• 1714 Drive not ready
• 1715 Track O indicator failure
• 1716 Diagnostics cylinder errors
• 1717 Surface read errors
• 1718 Hard drive type error
• 1720 Bad diagnostics cylinder
• 1726 Data compare error
• 1730 Controller error
• 1731 Controller error
• 1732 Controller error
• 1733 BIOS undefined error return
• 1735 Bad command error
• 1736 Data corrected error
• 1737 Bad track error
• 1738 Bad sector error
• 1739 Bad initialization error
• 1740 Bad sense error
• 1750 Drive verify failure
• 1751 Drive read failure
• 1752 Drive write failure
• 1753 Drive random read test failure
• 1754 Drive seek test failure
• 1755 Controller failure
• 1756 Controller Error Correction Code (ECC) test failure
• 1757 Controller head select failure
• 1780 Seek failure; drive 0
• 1781 Seekfailure; drive 1
• 1782 Controller test failure
• 1790 Diagnostic cylinder read error; drive 0
• 1791 Diagnostic cylinder read error; drive 1
• Hard disk configuration error
• Hard disk 0 failure
• Invalid drive specification
• Error selecting drive
• Invalid command interpreter
• No boot device available
• Missing operating system
• General failure reading drive C:
• Not ready reading drive C:
• A serious disk error occurred while trying to read/write drive C:
• Corrupt system files
• Hard Drive Circuitry Error
SCSI Hard Drive Failure Messages:
• 096xxxx SCSI adapter with cache (32-bit) errors
• 112xxxx SCSI adapter (16-bit without cache) errors
• 113xxxx System board SCSI adapter (16-bit) errors
• 210xxxx SCSI fixed disk errors
Here's some background information explaining what causes such errors:
When your system is turned on, your computer BIOS performs a power-on self test (POST). It does this to verify that everything is working properly on your PC. When the BIOS boots your system to the point that it gains access to its video subsystem, it displays the information about the PC during the booting process. It uses the video system to communicate error messages like those above.
Different parts of your system can launch an error message, depending upon how far the booting process has progressed. Most error messages originate from the system BIOS because it is responsible for most of the functions for booting up. Still, other physical errors can be relayed to the Operating System. Those error messages are usually related to your Operating System.
One reason you receive such an error message is that the BIOS cannot find the drive, or one of the drives was not specified in the CMOS setup. Make sure that all the floppy boot drives have been removed from your system because this could be the cause for the error message.
If you experience this kind of disk error failure, you should be very careful about how you react because you could permanently lose important data. After determining that the problem is the result of a disk drive, try to run some diagnostic tools as was mentioned above or contact a professional data-recovery specialist.
Reference:-http://hdddatarecovery.blogspot.com/
Jan 15, 2009
List of the Best Free Hard Disk Diagnostic Tools.
This is a diagnostic tool to help users quickly verify whether their Fujutsu hard drive is operating correctly. This diagnostic tool can diagnose your suspected faulty hard drive by checking the S.M.A.R.T. data and also by scanning the entire surface of the drive, sector by sector, to verify media integrity. FJDT can be also run from a bootable MSDOS diskette, which enables diagnosis even when the OS is not booting.
Download (62Kb)
Homepage
Fujitsu SCSI Diagnostics.
SCSI Diagnostics is a simple and reliable SCSI diagnostic tool developed by Fujitsu verifying the condition of your Fujitsu SCSI Hard Disk Drive. It checks S.M.A.R.T. information and performs a series of tests.
Download (737Kb)
Homepage
Fujitsu Windows Diagnostic Tool.
This diagnostic tool is available for use by users who feel their Fujitsu hard drive may not be operating normally. It is only designed for use with Fujitsu ATA/IDE hard drives. There are 2 diagnostic modes: Quick Test (about 3 minutes, does random seek/read tests) and Comprehensive Test (about 30 to 100 minutes, also performs surface scan).
Download (444Kb)
Homepage
IBM Hitachi Drive Fitness Test.
The Drive Fitness Test (DFT) provides a quick, reliable method to test SCSI and IDE hard disk drives. It analyzes drive fitness, restores drive fitness (contains the following utilities: Erase Bootsector, Low-level format, Filesystem-based Corrupted Sector Repair), displays drive information, etc.
Download (1.9Mb)
Homepage
Maxtor Powermax.
The Powermax utility is designed to perform diagnostic read/write verifications on Maxtor/Quantum hard drives. These tests will determine hard drive integrity. The Powermax utility is effective on all ATA (IDE) hard drives with a capacity greater than or equal to 500 MB. Warning: all data will be lost when the "Write Disk Pack (low level format)" test is performed.
Download (1Mb)
Maxtor SCSIMax.
SCSIMax is a diagnostic utility for all Maxtor/Quantum SCSI hard disk drives supporting Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T). This test will determine hard drive integrity in a short period of time, with a high degree of confidence.
Download (70Kb)
Quantum Data Protection System.
QDPS is a diagnostic utility for Quantum SCSI hard disk drives supporting S.M.A.R.T. technology.
Download (108Kb)
Seagate SeaTools for Windows.SeaTools for Windows has replaced SeaTools Online. SeaTools for Windows is a comprehensive, easy-to-use diagnostic tool that helps you quickly determine the condition of the disc drive in your external hard drive, desktop or notebook computer. It includes several tests that will examine the physical media on your Seagate disc drive and any non-Seagate disc drive. SeaTools for Windows tests USB, 1394, ATA (PATA/IDE), SATA and SCSI drives. It install onto your system. SeaTools for Windows is completely data safe. Requires Microsoft .NET Framework 2.0.
Download (6Mb)
Homepage
Western Digital Data Lifeguard.
Western Digital Data Lifeguard was written specifically for Western Digital EIDE hard drives. Its purpose is to examine the drive and test its functionality. It scans the drive and looks for errors. It even has the ability to correct certain types of errors that it may encounter. A Data Lifeguard Tools disk can be created.
Download (1.5Mb)
Homepage
Western Digital Data Lifeguard for Windows.
This is a Windows version of the Data Lifeguard Diagnostics utility. The utility can perform drive identification, diagnostics, and repairs on a Western Digital FireWire, EIDE, or USB drive. In addition, it can provide you with the drive's serial and model numbers.
Download (4Mb)
Homepage
Samsung Diagnostic (SHDiag).
This program is used to diagnose the disk when the SAMSUNG hard disk (supported models) is suspected to have failures. It is strongly recommended to back up your data before using this program.
Download (70Kb)
Homepage
reference:-http://hdddatarecovery.blogspot.com
Home Method for Hard Disk Data Recovery.
Hold the drive upside down, making gravity change the head geometry ever so slightly. Vertical is also another option.
Slightly rap the drive with your knuckle, (but nowhere near hard enough to damage the drive).
Try the drive in another machine, (slight drive voltage change assumed to be the miracle worker here).
Rap the drive just SLIGHTLY harder than you did above in 2.
Freeze the hard drive in the freezer for two hours, and place in a plastic zip lock bag to prevent condensation from forming on the drive when you plug it back into the system,
After the drive warms up to room temperature or better, rap it even harder with your knuckle this time.
Repeat all of above steps on next day, as sometimes I've gotten data off drive simply by trying again.
Reference:-http://hd-data-recovery.blogspot.com
Lost Data Recovery.
"last night I have installed HP Recovery Software in ma Laptop,
when I restart ma laptop then ma HDD fail to boot [all data & partion deleted including OS]
I m having importanlt DATA in HDD. Now how to recover ma DATA from HDD with partion & OS. [I have pluged that HDD in other laptop but it shows only one partion]"
Answer:
There's a lot of good data recovery software available, i use Power Data Recovery to pull off the job... Seagate has tools too, if you have lost your partitions you could go for partition recovery software like Active Partition Recovery.
For Your Help There are some software which Helps You.
1. Active Partition Recovery 3.0 - To Recover a Deleted partition.
2. Active Uneraser 3.0 - To recover deleted files and folders on FAT and NTFS systems.
3. Ontrack Easy Recovery Pro 6.10 - To Recover data that has been deleted/virus attack
4. Winternals Disk Commander 1.1 - More than just a standard deleted-file recovery utility
5. TestDisk 6.9b - Tool to check and undelete partition.
6. Lost & Found 1.06 - a good old data recovery software.
7. DiyDataRecovery Diskpatch 2.1.100 - An excellent data recovery software.
8. Prosoft Media Tools 5.0 v1.1.2.64 - Another excellent data recovery software with many
other options.
9. PhotoRec 6.9b - File and pictures recovery Tool.
Reference:-http://hd-data-recovery.blogspot.com
Jan 14, 2009
Hard Drive Problem [ BOOT ERROR].
If You Have Any Solution Give Yours Opinion In Comments.
System configuration:
Intel Dual Core 3.0 GHz
Windows XP Prefessional SP2
1.5 GB Ram
Lite-On DVD-Writer
SMTP= Intex
Hardisk - 160 GB Sata Seagate (barracuda)
Graphics Card - ATI inbuilt (Shared memory)
Problem.
Hard-disk 160gb crashed. Windows wont start. Re-insert bootable media.
possible cause = maybe some jerk has caused this fatal error. Cause is unknown, but it is being detected in the BIOS, but wont work otherwise.
History
I tried a number of ways to get it right.
tried to use it as Slave to a bootable working master, with the master working in Safe mode or normal mode. (but the master wont boot, if this drive is connected in slave).
Tried to work it in safe mode, still no results. it wont go further form "Mup.sys" (god knows what it is)
Tried the Ultimate Boot Disk (freeware). Tried to boot from that, even that couldnt detect it... (well im still working on that).
Went online to check how to integrate a Hardisk utility software inot the Ultimate Boot Disk.
They told me about an Add-on called TEST-Partition, which could repair my drive. well, i went to the offered Link, but there were no instructions as to how i can integrate that tool into the ultimate boot disk? and how can i use it in DOS mode. there was only a download link, and how to use it. No integration with UBD was provided on its website.
Anyways, i tried the NTFS-Dos compatibility mode, (some 10 mins back), in the UBD itself (by deafult), and this is the error that it gave me:
" Hard disk1 Size= 156290904 KB
Hard Disk Partition Not found by Xp_Shell!A:\ "
well, this made me feel a little better, and I believe that integrationg that Test-Partition utility with the UBD might give better results.... since that tool is dedicated to Repairing Partitions alone.
So now, i need to know, where i could have gone wrong. and how can i integrate the Test-partition utility with the UBD.
UBD= Ultimate Boot disk (still in Multi-session)
Ive checked the Power and data cables - they work fine with the other Sata hardisk.
For the UBD, i even tried to use hardisk in Legacy mode, still no results.
Solution:
A simple Solution just reinstall xp. Lolz.
either you can also use Hiren's Boot CD.
u can either try to boot with win xp cd and use the repair console to try maybe chkdsk or such
if not, try booting w/ the other working HDD alone, then connect the faulty one via usb(u can get an ide>usb adapter cheaply) this way it should be recognized
then either back your hard drive or re-patch the booting/system files.
Data Recovery. A Solution.
There are two basic methods you can go when it comes to hard drive retrieval: Using a professional person in data recovery center, or a do it your self utility. Software are much more sparing to use than a service provider company, but they are less reliable than using a professional for obvious reasons. My part is to help you choosing which one suites you best.
Software verses Service.
What I have found out over the years is that almost everyone wants to try hard drive data recovery software, because it is cheaper, quicker, and private. That blogs, some users have no business using hard drive recovery software, because they make matters more regretful by not understanding the fundamental setup and recovery steps.
The cry from technicians to make more sophisticated hard drive recovery tools has also caused an increase in the number of hard drive casualties. This is because the more damage that can occur. Yes, these powerful programs can recover more data, but if you do not know the proper methode, they can also destroy remaining data.
Development Or Research.
I have had many conversations over the years with colleagues from various hard drive recovery centers about what level of software they want us to develop, and how much of the program should be offered to the public. There have been two reasons I have researched this topic:
First, is for economical reasons. plainly, the cheaper the software, the more people will use these hard drive recovery tools. The more powerful the utility, the less need the public has for sending their drive to a hard drive recovery service. Because we also develop tools for these firms, we have to balance pleasing both groups of users, which at times can be a challenging task.
The next reason for this research is for data safety. In other words, how much do we need to protect you from yourself? We truly want you to recover your own data, and helping you prevent undoable is part of the process. I say this because invariably I (and other service companies) get drives weekly that have been trashed by misusing software utilities. As a consequence, many of these drives are considered unrecoverable.
Defining the fine line between offering you cutting edge technologies in the form of software, and making you send your drive to an expert to protect your data from your possible fatal mistakes. I say this because I know you want to try the data-recovery yourself - at least as the first step.
Your Next Step.
While you do not want to delay in getting your data back, you also want to take the right steps to protect your data. I want you to be asking yourself, "Can I do this myself, I use a hard drive recovery professional?" If you are not sure, get help. You know your capabilities, and by reading this information, you will probably know which solution is best for you.
Jan 13, 2009
Hard drive data recovery.

A faulty circuit board is characterize by a drive that does not 'spin up', meaning that platters are not turning underneath the copper wire. A faulty actuator arm or more serious mechanical error is characterize by an abnormal clicking noise or a grinding noise.The best advise in determining whether you have a hardware problem is to listen to the sound of your hard drive. If you cannot hear the platters spinning (i.e. it is quiet when it is turned on) or you hear more serious noises then you should stop using the drive immediately and you will need to send your drive to a hardware data recovery service.
Hardware data recovery can be expensive because technicians may need to disassemble your hard drive to fix the problem. Hard drive data recovery is usually done in a 'clean room' as hard drives are sealed to avoid errors caused by dust or other particles. Also hard drives are finely tuned machinery and it takes specialist equipment to read the platters from a physically damaged drive.
Jan 12, 2009
Recover a Busted External Hard Drive.
My wife kicked my 500 GB Western Digital external hard drive onto the ground and it stopped working. When you plug it in, it clicks repeatedly and never works.
I have tried freezing the drive, removing the SATA drive inside and installing it directly into the PC, and shaking it and crying, and none of these things have worked.
Is there a way to recover the data on this drive without paying a lot of money and risking being thrown in prison for pirated software?
Answer:
well with that kind of damage i doubt so. If it is truely un-readable then its dead. If it were a 2.5" one then possibly or it may still work. 3.5" inches are less durable and not meant to be moved around too much.
if you know how to use hardware as in opening insides, etc.
you have to find another of the same drive then open em both up.
check your disk 1st, see if the cylinders are broken, if the cylinders are broken, then there's no way to receover data; if not then open the other one and just replace the cylinders in urs with the new hd, then put the new hd together and plug it in, if you did all good, it should work;best take it to a computer shop who knows how to replace cylinders and they can help you find the same hd as well.
good luck.
Reference:-http://hd-data-recovery.blogspot.com
How to Recover Data from the Hard Drive of a Dead Laptop.
1. Purchase a "Laptop Hard Drive Adaptor Kit" to allow you to plug your laptop hard drive into a standard PC (2.5 TO 3.5 inch IDE HDD).
2. Find a functioning standard PC that can read the file system that was on the laptop. One would need Windows 2k/XP or a Linux distribution to read an NTFS/FAT file system, whereas only a Linux distribution can read the EXT3 file system.
3. Open up the case and add the laptop drive with adaptor kit as a secondary HDD. Be sure that you have set this drive to either Cable Select, or Slave, depending on the configuration of the system, and the available IDE ports.
4. Copy the data you need from the laptop drive to the main drive of the PC, or consider using removable storage for small files.
Method. 2
1. Purchase or cannibalize a 2.5" USB 2.0 or Firewire drive enclosure.
2. Find a functioning standard PC with an open USB port (or firewire port, as applicable) that can read the file system that was on the laptop. One would need Windows 2k/XP or a Linux distribution to read an NTFS/FAT file system, whereas only a Linux distribution can read the EXT3 file system.
3. Plug it in, wait for the tones (and/or mount it if that is necessary in this system)
4. Copy the data you need from the laptop drive to the main drive of the PC, or consider using removable storage for small files.
Reference:-http://hd-data-recovery.blogspot.com
FREEZING HARD DRIVE FOR RECOVERY.
What do you guys think? Myth or reality? It seems that a lot of people agree that this solution actually works, so I decided to test it myself with an old Maxtor hard drive that failed me a couple of weeks ago. There was no important data on there, so losing the disk didn't really bother me.
Before putting it in the freezer, the drive was making a weird clicking noise, and the computer was showing me this message: Primary hard drive 0 not found, strike F1 to retry boot, F2 to run the setup utility.
I removed the hard disk from the computer and sealed it in a ziplock bag to prevent condensation.
After this, I shoved it in the freezer, and waited an hour.
I finally installed it back in the computer, closed the case, and pushed on the power button.
YES! it works, the computer is starting correctly! Unfortunately, after I logged in, Windows froze and I wasn't able to do anything. I tried rebooting, and....
Well, at least the hard disk spun for about 2 minutes before crashing again. Maybe that's not long enough to let me recover any data, but it worked for a little while. :)
edit: The day after, I shoved the hard drive back in the freezer for 24 hours. After getting it out, I was able to get 20 more minutes of life out it.
Reference:-http://hd-data-recovery.blogspot.com
How to Open Laptop Disk for Data Recovery ?
1. Turn off the computer power.
2. Unplug the power cord.
3. Remove the battery.
4. Turn the notebook over, then remove the main and optional secondary batteries
5. Remove the hard drive screw, then pull the hard drive kit straight out from the notebook.
 Remove the screws that attach the hard drive to the hard drive tray and Keep aside the screws, as you will be using them later to reconnect the disk.
Remove the screws that attach the hard drive to the hard drive tray and Keep aside the screws, as you will be using them later to reconnect the disk.
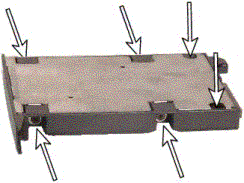
Remove the hard drive from the hard drive tray/caddy/case.
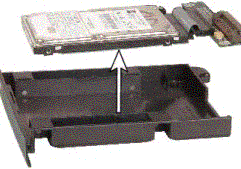
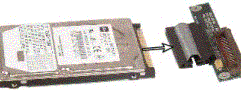
Now your hard drive is free to perform data recovery using our software.
To connect laptop disk to desktop pc you require a connector,
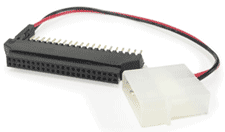
OR
http://www.datapro.net/products/1920.html
Now download and install our demo data recovery software depending upon the disk from which you want to recover the data, download the required demo from the link file recovery software demo.
Hard Disk Bad Sector Recovery.
Hard Drive Data Recovery.
Jan 10, 2009
Simply Recovery of Data from a Dead Hard Drive.
 On a Mac, the process is so simpler. Use a FireWire cable for hooking your nonworking Mac to a working Mac, then, “target boot” the nonworking machine by holding down the T key as you power it on. With either method, it’s possible that your failed hard drive will show up on your healthy computer and reveal its files, in which case your hard drive is probably fine, but your operating system needs to be reinstalled. (Don’t forget to offload your files before you do that.)
On a Mac, the process is so simpler. Use a FireWire cable for hooking your nonworking Mac to a working Mac, then, “target boot” the nonworking machine by holding down the T key as you power it on. With either method, it’s possible that your failed hard drive will show up on your healthy computer and reveal its files, in which case your hard drive is probably fine, but your operating system needs to be reinstalled. (Don’t forget to offload your files before you do that.)
If your files don’t show up on the secondary computer, then you are at one of those pivotal moments in life when you find out how much your hard work and treasured memories are really worth to you. Depending on how your drive is damaged, an attempt to salvage your data can cost anywhere from a hundred dollars to several thousand. What’s more, the process can take days—and there is no guarantee that the money and time you invest will produce any results whatsoever.
Now that we’ve gone through the depressing task of properly setting your expectations, here’s the good news: Very often, the data on failed drives is recoverable. In fact, it’s surprising how resilient that information can be—just ask any corporate embezzler who thought he had deleted all the evidence from his PC, only to have it show up later in court. The comparison is apt, since the very same computer forensic tools that uncover digital misdeeds are the ones that can find your treasured family photos.
There are two ways that drives crash: Logical failure and mechanical failure. In a logical failure, the drive’s components are physically undamaged, but because of either accidental formatting or a corrupt file system, the drive is not able to find and navigate its own data. However, unless it has been overwritten, that data still exists on your drive.
A mechanical failure means that your drive has broken parts that are preventing it from working busted drives often make a telltale clicking sound as they futilely attempt to access their files. If you hear that, your data may still be there, but you’re not getting it back without calling in the experts (see “Worst-Case Scenario,” next page). And those experts make good money. Data recovery services from Kroll Ontrack, Seagate’s i365 and Iomega charge between $500 and $2500 to attempt to salvage data from either logical or mechanical disasters, depending on the severity of the situation. But if you are just dealing with a logical failure, you can get your files back on your own for far less.
Recovering a hard drive is a bit like getting back a stolen car—you’ll be happy to have your files back, but the results could be messy. No data recovery program will return your files to you in exactly the condition you originally kept them. These programs are designed to essentially do a data dump from your problem drive to a new drive. Files will be organized by type (JPEG images will be in one folder, Word documents in some other folder, MPEG movies in another) and your songs and photos will be mixed with random sound and image files from your computer’s system folder.
Additionally, the names of all your files will have been changed to various alphanumeric sequences, such as IMG1039.jpg or MOV2010.mov. So be prepared to settle in for a long weekend of sifting through and renaming your files. Oh, and while you’re at it, now’s a good time to buy that backup drive.
Reference:-http://hd-data-recovery.blogspot.com/search/label/Hard%20Disk%20Recovery%20Articles
Jan 6, 2009
Data Recovery Software
You can preview most of the files found by R-Studio DEMO version regardless of file size, but please note R-Studio Emergency DEMO doesn't support file preview option.
The DEMO versions can be registered on on-the-fly and no reinstallation required. When R-Studio Demo version has found a lost file larger than 64KB you may simply double click the file to preview it. If you are satisfied with the file content you may buy the R-Studio registration key, register the software and recover the file right away.
However, if there is enough disk space on any additional hard drive or on an alternative media we always recommend our customers to create an image of the recognized partition where the lost files were found, because Windows OS constantly writes some information on disks and there is a risk that the sectors where the deleted files reside may be overwritten. If that happens, the files still may be found, but may contain incorrect data or cannot be found at all. The created image can be processed the same way as the original partition.
Reference:-http://hd-data-recovery.blogspot.com/search/label/Hard%20Disk%20Recovery%20Softwares
